Node packages that will make you more productive every day

Node.js is great for reusing code — and the backbone of reusing code is NPM packages.
NPM packages save us tons of time and effort. Need a date library? There’s a package for it. Need a utility library? No problem, just install the package. Whenever you need to solve a problem with code, the chances are there’s a package tailored to your needs.
Here’s a list of packages I think every Node.js developer should know. Treat these NPM packages as time savers and magic fairy helpers.
husky
Husky makes it straightforward to implement git hooks. Work with a team and want to enforce coding standards across the team? No problem! Husky lets you require everyone to automatically lint and tests their code before committing or pushing to the repository.
How to install
yarn add huskyUsage
Here’s an example of how you can implement husky hooks:
// package.json
{
"husky": {
"hooks": {
"pre-commit": "npm lint",
"pre-push": "npm test"
}
}
}The pre-commit hooks will run before you commit to the repository.
The pre-push hook runs before you push the code to the repository.
dotenv
Dotenv is a zero-dependency module that loads environment variables from a
.envfile intoprocess.env. Storing configuration in the environment separate from code is based on The Twelve-Factor App methodology.
How to install
yarn add dotenvUsage
As early as possible in your application, require and configure dotenv:
require('dotenv').config()Create a .env file in the root directory of your project. Add environment-specific variables on new lines in the form of NAME=VALUE. For example:
DB_HOST=localhost
DB_USER=root
DB_PASS=s1mpl3process.env now has the keys and values you defined in your .env file:
const db = require('db')
db.connect({
host: process.env.DB_HOST,
username: process.env.DB_USER,
password: process.env.DB_PASS
})date-fns
Date-fns is like lodash, but for dates. It includes many utility functions that make it easier to work with dates.
date-fns provides the most comprehensive, yet simple and consistent toolset
for manipulating JavaScript dates in a browser & Node.js.
How to install
yarn add date-fnsUsage
Here’s a quick sample of the date-fns library:
import { compareAsc, format } from 'date-fns'
format(new Date(2014, 1, 11), 'yyyy-MM-dd')
//=> '2014-02-11'
const dates = [
new Date(1995, 6, 2),
new Date(1987, 1, 11),
new Date(1989, 6, 10),
]
dates.sort(compareAsc)
//=> [
// Wed Feb 11 1987 00:00:00,
// Mon Jul 10 1989 00:00:00,
// Sun Jul 02 1995 00:00:00
// ]Bunyan
Bunyan is an easy-to-grasp and performant JSON logging library for Node.
How to install
yarn add bunyanTip: The bunyan CLI tool is written to be compatible (within reason) with all versions of Bunyan logs. Therefore you might want to yarn add global bunyan to get the Bunyan CLI on your PATH, then use local Bunyan installs for node.js library usage of Bunyan in your apps.
Usage
Bunyan is a simple and fast JSON logging library for node.js services.
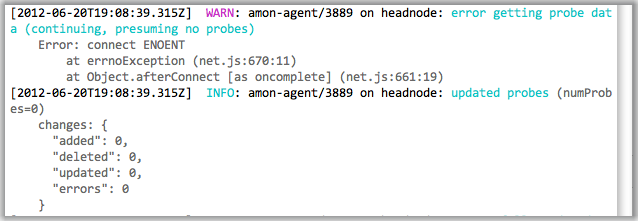
// hi.js
const bunyan = require('bunyan');
const log = bunyan.createLogger({name: "myapp"});
log.info("hi");Here’s what’s being returned to the console if you run node hi.js.
Ramda
Rambda is a practical, functional, utility library for JavaScript programmers. Ramda emphasizes a purer functional style.
Immutability and side-effect free functions are at the heart of Ramda’s design philosophy. This can help you get the job done with simple, elegant code.
How to install
$ yarn add ramdaUsage
import * as R from 'ramda'
<strong>const</strong> greet = R.replace('{name}', R.__, 'Hello, {name}!');
greet('Alice'); //=> 'Hello, Alice!'debug
Debug is a tiny JavaScript debugging utility modeled after Node.js core’s debugging technique.
How to install
$ yarn add debugUsage
debug exposes a function — simply pass this function the name of your module and it will return a decorated version of console.error for you to pass debug statements to.
How to install
yarn add debugUsage
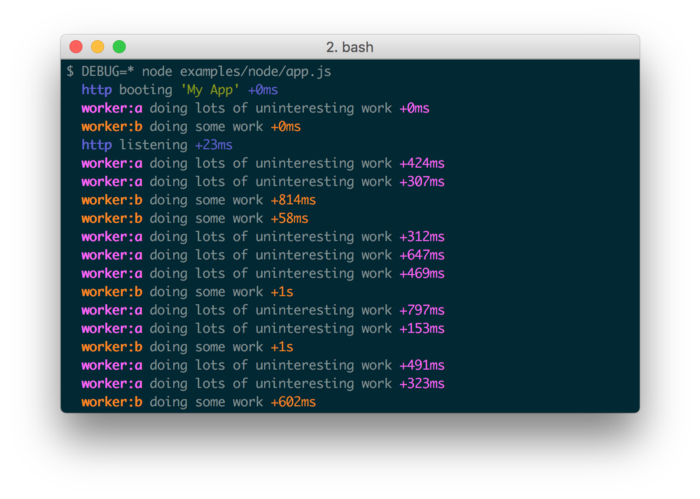
const debug = require('debug');
const log = debug('http:server');
const http = require('http');
const name = 'My App name';
log('booting %o', name);
http.createServer((req, res) => {
log(req.method + ' ' + req.url);
res.end('debug examplen');
}).listen(3200, () => {
log('listening');
});
// run this command in the terminal
// DEBUG=http:server node app.jsThis will allow you to toggle the debug output for different parts of your module as well as the module as a whole.
flat
flat takes a nested Javascript object and flattens it. You can also unflatten an object with delimited keys.
Installation
$ yarn add flatUsage
const flatten = require('flat')
flatten({
key1: {
keyA: 'valueI'
},
key2: {
keyB: 'valueII'
},
key3: { a: { b: { c: 2 } } }
})
// {
// 'key1.keyA': 'valueI',
// 'key2.keyB': 'valueII',
// 'key3.a.b.c': 2
// }JSON5
The JSON5 Data Interchange Format (JSON5) is a superset of JSON that aims to alleviate some of the limitations of JSON by expanding its syntax to include some productions from ECMAScript 5.1.
How to install
yarn add json5
const JSON5 = require('json5')Usage
Notice the file extension. JSON5 is an extension and superset of JSON.
{
// comments
unquoted: 'and you can quote me on that',
singleQuotes: 'I can use "double quotes" here',
lineBreaks: "Look, Mom! \
No \n's!",
hexadecimal: 0xdecaf,
leadingDecimalPoint: .8675309, andTrailing: 8675309.,
positiveSign: +1,
trailingComma: 'in objects', andIn: ['arrays',],
"backwardsCompatible": "with JSON",
}ESLint
ESLint is a wonderful tool for avoiding bugs and forcing coding standards for development teams. ESLint is a tool for identifying and reporting on patterns found in ECMAScript/JavaScript code.
How to install and use
$ yarn add eslintYou should then set up a configuration file:
$ ./node_modules/.bin/eslint --initAfter that, you can run ESLint on any file or directory like this:
$ ./node_modules/.bin/eslint yourfile.jsFor further explanations, please refer to the official documentation. There are lots of examples of getting started and configuration.
PM2
PM2 is a production process manager for Node.js applications with a built-in load balancer. It allows you to keep applications alive forever, to reload them without the downtime, and to facilitate common system admin tasks.
Installing PM2
$ yarn add global pm2Start an application
You can start any application (Node.js, Python, Ruby, binaries in $PATH…) like so:
$ pm2 start app.jsYour app is now daemonized, monitored, and kept alive forever.
Managing Applications
Once applications are started you can manage them easily. Here’s how you can list all running applications:
$ pm2 ls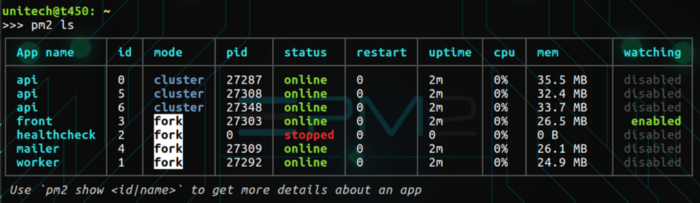
Helmet
The Helmet library helps you with securing your Express apps by setting various HTTP headers. “It’s not a silver bullet, but it can help!”
How to install
yarn add helmetUsage
Helmet is Connect-style middleware, which is compatible with frameworks like Express. (If you need support for Koa, see koa-helmet.)
<strong>const</strong> express <strong>=</strong> require("express");
<strong>const</strong> helmet <strong>=</strong> require("helmet");
<strong>const</strong> app <strong>=</strong> express();
app.use(helmet());The top-level helmet function is a wrapper around 11 smaller middleware. In other words, these two things are equivalent:
// This...
app.use(helmet());
// ...is equivalent to this:
app.use(helmet.contentSecurityPolicy());
app.use(helmet.dnsPrefetchControl());
app.use(helmet.expectCt());
app.use(helmet.frameguard());
app.use(helmet.hidePoweredBy());
app.use(helmet.hsts());
app.use(helmet.ieNoOpen());
app.use(helmet.noSniff());
app.use(helmet.permittedCrossDomainPolicies());
app.use(helmet.referrerPolicy());
app.use(helmet.xssFilter());compression
The compression library is a Node.js compression middleware.

How to install
$ yarn add compressionUsage
When using this module with express or connect, simply call compression with express middleware. Requests that pass through the middleware will be compressed.
const compression = require('compression')
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
// compress all responses
app.use(compression())
// ...By: Indrek Lasn
Retrieved by: https://medium.com/better-programming/12-useful-packages-every-node-js-developer-should-know-2746db760e
- How to Run a Company Hackathon - 27 de Maio, 2021
- 12 Useful Packages Every Node.js Developer Should Know - 7 de Setembro, 2020
- How Chatbots Could Support Students and Enhance Remote Learning - 7 de Agosto, 2020
